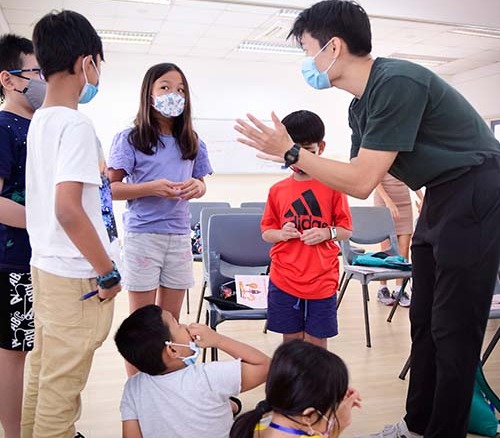
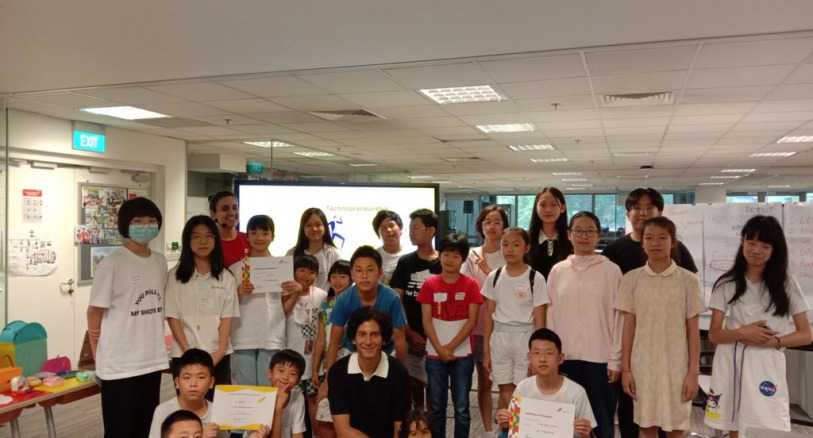
Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that encourages creativity and empathy. It is a process for creating innovative solutions to complex problems by involving users, prototyping and testing. This manual is aimed at helping teachers introduce design thinking to children, ages 8-12, in a fun and engaging way.

Lesson 1: Understanding the Design Thinking Process
- Introduction to design thinking and its five stages: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, Test.
- Discuss real-world examples of design thinking in action.
- Have students brainstorm a problem they have experienced, and walk them through the five stages of design thinking to come up with a solution.
Lesson 2: Empathize
- Discuss empathy and how it is important in design thinking.
- Have students practice empathy by interviewing classmates, family members, or friends about a problem they have faced.
- Have students share their findings and discuss how they can use this information to design a solution.
Lesson 3: Define
- Discuss the importance of defining the problem clearly.
- Have students use their findings from the empathy stage to create a problem statement.
- Lead a class discussion on how to refine the problem statement and ensure it is clearly defined.
Lesson 4: Ideate
- Introduce the idea of brainstorming and encourage students to come up with as many ideas as possible.
- Have students work in groups to brainstorm solutions to the problem they defined in the previous lesson.
- Encourage students to be creative and not limit their ideas.
Lesson 5: Prototype
- Discuss the importance of prototyping and why it is a key stage in the design thinking process.
- Have students select one of their ideas from the ideation stage and create a prototype using materials such as cardboard, paper, or clay.
- Encourage students to think about how they can make their prototypes more realistic or functional.
Lesson 6: Test
- Discuss the importance of testing and how it helps refine the solution.
- Have students test their prototypes and gather feedback from classmates, family members, or friends.
- Lead a class discussion on how to use the feedback to improve the prototypes.
Conclusion: Design thinking is a powerful tool that can help children develop critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills. By following these lessons, teachers can introduce design thinking to children in a fun and engaging way and help them develop these important skills. Encourage students to continue to use the design thinking process in their daily lives, and challenge them to come up with solutions to problems they encounter.